Technical Data
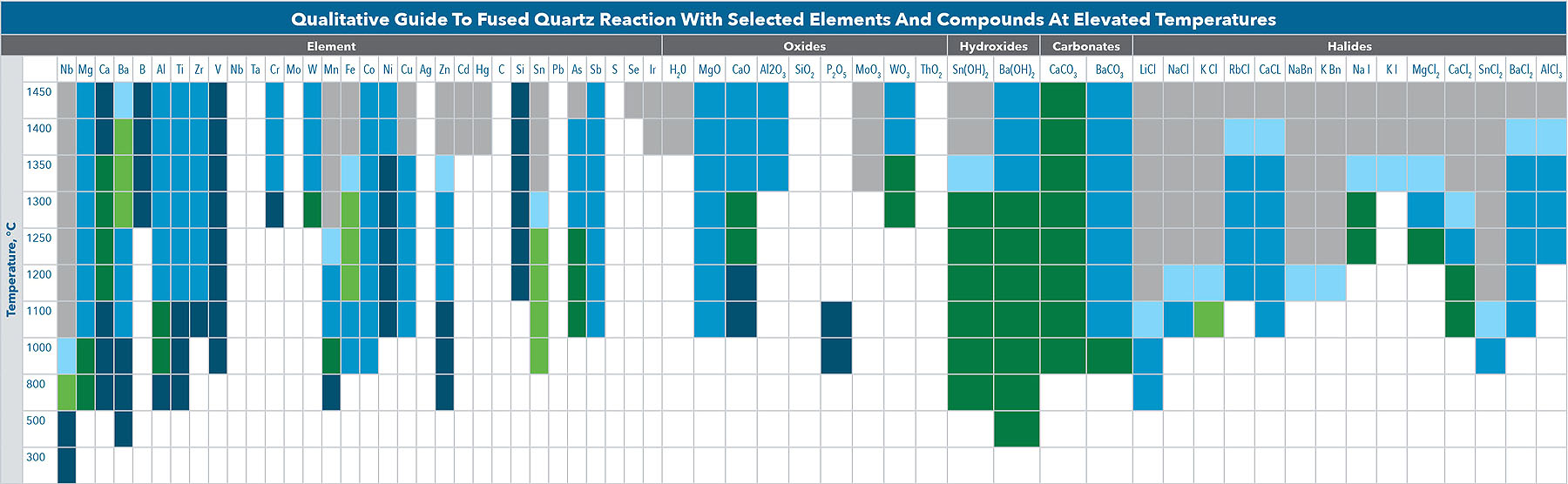
Reactivity Chart
The effects of various elements and compounds on fused quartz at elevated temperatures are observed in a vacuum. Each sample, as shown in the reactivity table, is held at the lowest temperature for one hour, then at the next higher temperature for an hour, and so on. The extent of the reaction is, of course, also time-dependent.